causes and how to solve male infertility or low sperm count.
 Overview
Overview
If you and your partner are struggling to have a baby, you're not alone. Ten to 15 percent of couples in the United States are infertile. Infertility is defined as not being able to get pregnant despite having frequent, unprotected sex for at least a year for most couples.
Infertility may result from an issue with either you or your partner, or a combination of factors that interfere with pregnancy. Fortunately, there are many safe and effective therapies that significantly improve your chances of getting pregnant.
Symptoms
The main symptom of infertility is not getting pregnant. There may be no other obvious symptoms. Sometimes, an infertile woman may have irregular or absent menstrual periods. Rarely, an infertile man may have some signs of hormonal problems, such as changes in hair growth or sexual function.
Most couples will eventually conceive, with or without treatment.
Causes
-
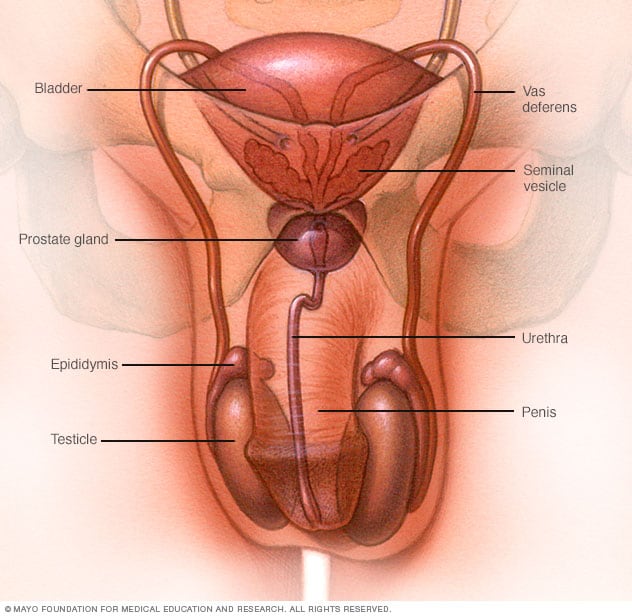
Male reproductive system
-
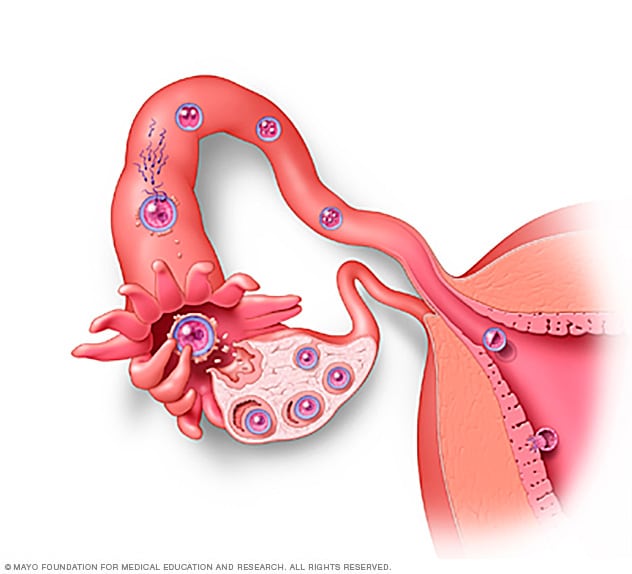
Fertilization and implantation
Infertility causes can affect one or both partners. In general:All of the steps during ovulation and fertilization need to happen correctly in order to get pregnant. Sometimes the issues that cause infertility in couples are present at birth, and sometimes they develop later in life.
- In about one-third of cases, there is an issue with the male.
- In about one-third of cases, there is an issue with the female.
- In the remaining cases, there are issues with both the male and female, or no cause can be identified.
Causes of male infertility
These may include:
- Abnormal sperm production or function due to undescended testicles, genetic defects, health problems such as diabetes or infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, mumps or HIV. Enlarged veins in the testes (varicocele) can also affect the quality of sperm.
- Problems with the delivery of sperm due to sexual problems, such as premature ejaculation; certain genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis; structural problems, such as a blockage in the testicle; or damage or injury to the reproductive organs.
- Overexposure to certain environmental factors,such as pesticides and other chemicals, and radiation. Cigarette smoking, alcohol, marijuana or taking certain medications, such as select antibiotics, antihypertensives, anabolic steroids or others, can also affect fertility. Frequent exposure to heat, such as in saunas or hot tubs, can raise the core body temperature and may affect sperm production.
- Damage related to cancer and its treatment, including radiation or chemotherapy. Treatment for cancer can impair sperm production, sometimes severely.
Risk factors
Many of the risk factors for both male and female infertility are the same. They include:
- Age. A woman's fertility gradually declines with age, especially in her mid-30s, and it drops rapidly after age 37. Infertility in older women may be due to the number and quality of eggs, or to health problems that affect fertility. Men over age 40 may be less fertile than younger men are and may have higher rates of certain medical conditions in offspring, such as psychiatric disorders or certain cancers.
- Tobacco use. Smoking tobacco or marijuana by either partner reduces the likelihood of pregnancy. Smoking also reduces the possible benefit of fertility treatment. Miscarriages are more frequent in women who smoke. Smoking can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction and a low sperm count in men.
- Alcohol use. For women, there's no safe level of alcohol use during conception or pregnancy. Avoid alcohol if you're planning to become pregnant. Alcohol use increases the risk of birth defects, and may contribute to infertility. For men, heavy alcohol use can decrease sperm count and motility.
- Being overweight. Among American women, an inactive lifestyle and being overweight may increase the risk of infertility. A man's sperm count may also be affected if he is overweight.
- Being underweight. Women at risk of fertility problems include those with eating disorders, such as anorexia or bulimia, and women who follow a very low calorie or restrictive diet.
- Exercise issues. Insufficient exercise contributes to obesity, which increases the risk of infertility. Less often, ovulation problems may be associated with frequent strenuous, intense exercise in women who are not overweight.
Prevention
Some types of infertility aren't preventable. But several strategies may increase your chances of pregnancy.
Couples
Have regular intercourse several times around the time of ovulation for the highest pregnancy rate. Having intercourse beginning at least 5 days before and until a day after ovulation improves your chances of getting pregnant. Ovulation usually occurs at the middle of the cycle — halfway between menstrual periods — for most women with menstrual cycles about 28 days apart.
Men
For men, although most types of infertility aren't preventable, these strategies may help:
- Avoid drug and tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption, which may contribute to male infertility.
- Avoid high temperatures, as this can affect sperm production and motility. Although this effect is usually temporary, avoid hot tubs and steam baths.
- Avoid exposure to industrial or environmental toxins, which can impact sperm production.
- Limit medications that may impact fertility, both prescription and nonprescription drugs. Talk with your doctor about any medications you take regularly, but don't stop taking prescription medications without medical advice.
- Exercise moderately. Regular exercise may improve sperm quality and increase the chances for achieving a pregnancy.
PRICE OF THE FERTILITY CLEANSING PACK 2450GHC








0 Comments